P168_Egypt
Revolutionizing Water Treatment with Predictive Machine Learning Modeling and Sustainable Adsorbents
Cooperating countries: Egypt and Austria
Coordinating institution: University for Continuing Education Krems, Martin Brandl martin.brandl@donau-uni.ac.at
Partner institution: Suez University
Project duration: 1 October 2025 - 30 September 2027
Budget: EUR 27.290
Abstract:
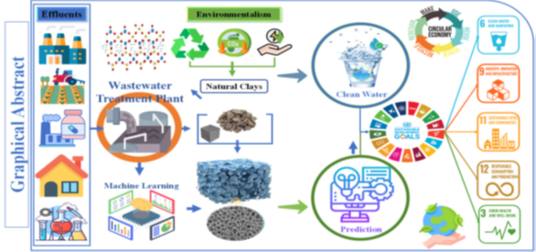
The increasing complexity of wastewater pollution necessitates innovative and sustainable treatment solutions. Our project, RWT-ML, proposes an advanced approach that integrates machine learning (ML) with composite or nanocomposite adsorbents derived from clay and polyamide press felts to enhance wastewater treatment efficiency. Machine learning algorithms will be utilized to predict pollution events, enabling proactive decision-making and optimizing treatment processes for improved performance. The development of novel adsorbents from these low-cost, abundant materials will support their application in both batch and continuous flow (column) systems, ensuring scalability and realworld feasibility. The synergy between ML-driven predictive modeling and sustainable adsorbents bridges the gap between theoretical advancements and practical implementation, enhancing the efficiency and adaptability of water treatment strategies. Furthermore, this project embraces circular economy principles by repurposing industrial by-products and natural resources, minimizing waste, and promoting sustainable practices. In alignment with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those related to clean water and sanitation, this initiative aims to establish a scalable and environmentally responsible model for wastewater management. Through interdisciplinary collaboration and innovative methodologies, RWT-ML seeks to drive a transformative shift in wastewater treatment, ensuring long-term resilience and sustainability in water ecosystems.